Summary
- Article Source: Modern Oil & Gas Architectures Built with Hadoop,
- Authors: Justin Sears
Modern Oil & Gas Architectures Built with Hadoop
By Justin Sears on March 6th, 2014
This is the sixth in our series on modern data architectures across industry verticals. Others in the series are:
- Modern Healthcare Architectures Built with Hadoop
- Modern Manufacturing Architectures Built with Hadoop
- Modern Telecom Architectures Built with Hadoop
- Modern Retail Architectures Built with Hadoop
- Modern Advertising Architectures Built with Hadoop
The United States is enjoying resurgent fossil fuel production. In fact, the International Energy Agency estimates that by 2016, the U.S. will surpass Saudi Arabia and Russia to become the world’s largest oil producer. At the same time, total world oil production has ceased to expand.
These fundamental changes in the global hydrocarbon markets drive more production to a focus on shale and other less-accessible deposits. Universal changes in the availability of data are also underway, changing the petrochemicals business in ways similar to changes in telecom, retail and manufacturing.
Advances in instrumentation, process automation, and collaboration multiply the available volume of new types of data like sensor, geolocation, weather and seismic data. These can be combined with “human-generated” data like market feeds, social media, email, text, and images for new insight.
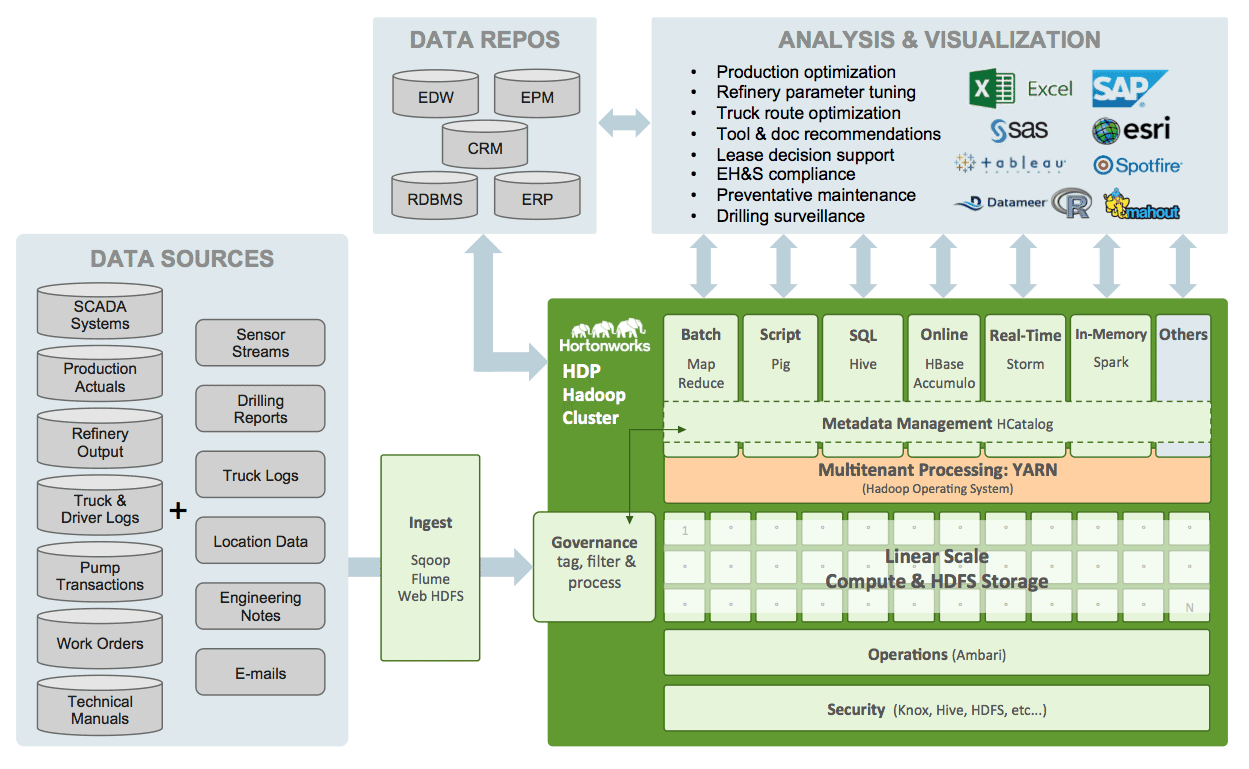
Oil and Gas does Hadoop.
This reference architecture shows how some of our oil and gas customers use Apache Hadoop to make the most of these changes.
The following are some specific oil and gas use cases (upstream, midstream, downstream or in oil field services). These show ways Apache Hadoop helps companies deliver oil and gas more quickly, more cost-effectively and with higher output.
Slow Decline Curves with Production Parameter Optimization
Oil companies need to manage the decline in production from their existing wells, since new discoveries are harder and harder to come by. Decline Curve Analysis (DCA) uses past production from a well to estimate future output.
However, historic data usually shows constant production rates, whereas a well’s decline towards the end of its life follows a non-linear pattern—it usually declines more quickly as it depletes. When it comes to a well near the end of its life, past is not prologue.
Production parameter optimization is intelligent management of the parameters that maximize a well’s useful life, such as pressures, flow rates, and thermal characteristics of injected fluid mixtures. Machine learning algorithms can analyze massive volumes of sensor data from multiple wells to determine the best combination of these controllable parameters.
This analysis helps the well’s owner or lessee make the most of that resource.
Define Operational Set Points for Each Well & Receive Alerts on Deviations
After identifying the ideal operating parameters (e.g. pump rates or fluid temperatures) that produce oil and gas at the highest margins, that information can go into a set point playbook.
Maintaining the best set points for a well in real-time is a job for Apache Storm’s fault-tolerant, real-time analytics and alerts. Storm running in Hadoop can monitor variables like pump pressures, RPMs, flow rates, and temperatures, then take corrective action if any of these set points deviate from pre-determined ranges.
This data-rich framework helps the well operator save money and adjust operations as conditions change.
Optimize Lease Bidding with Reliable Yield Predictions
Oil and gas companies bid for multi-year leases to exploration and drilling rights on federal or private land. The price paid for the lease is the known present cost paid to access a future, unpredictable stream of hydrocarbons.
The well lessor can outbid his competitors by reducing the uncertainty around that future benefit and more accurately predicting the well’s yield. Apache Hadoop can provide this competitive edge by efficiently storing image files, sensor data and seismic measurements. This adds missing context to any third-party survey of the tract open for bidding.
The company that possesses that unique information can now pass on a lease that they might otherwise have pursued, or they can find “diamonds in the rough” and lease those at a discount.
Report on Compliance with Environmental, Health and Safety Regulations
Compliance with EH&S regulations serves both near-term and long-term objectives. In the short run, compliance avoids fines and improves the company’s corporate reputation. Over the long haul, a pattern of compliance reduces the risk of catastrophic incidents.
Apache Hadoop is an ideal platform for a secure data lake that contains compliance-related data in many formats. Improved data capture and retention make compliance reporting easier.
Because Hadoop does not require “schema on load”, oil and gas companies can store data in its raw form and in all of its formats: pdf documents, videos, sensor data, or structured ERP data.
Then only the relevant information need be queried for each report. This versatility lets a corporation respond nimbly to changes in regulations or to requests for information.
Repair Equipment Preventatively with Targeted Maintenance
Traditionally, operators gathered data on the status of pumps and wells through physical inspections (often in remote locations). This meant that inspection data was sparse and difficult to access, particularly considering the high value of the equipment in question and the potential health and safety impacts of accidents.
Now sensor data can stream into Hadoop from pumps, wells and other equipment much more frequently—and at lower cost—than collecting the same data manually. This helps guide skilled workers to do what sensors cannot: repair or replace machines. The machine data can be enriched with other data streams on weather, seismic activity or social media sentiment, to paint a more complete picture of what’s happening in the field.
Algorithms then parse that large, multifaceted data set in Hadoop to discover subtle patterns and compare expected with actual outcomes. Did a piece of equipment fail sooner than expected, and if so, what similar gear might be at risk of doing the same?
Data-driven, preventative upkeep keeps equipment running with less risk of accident and lower maintenance costs.
Integrate Exploration with Seismic Image Processing
An article in Forbes in May 2013 entitled Big Data and Microseismic Imaging Will Accelerate the Smart Drilling Oil and Gas Revolution summed up the importance of seismic information management like this:
“Although horizontal drilling and hydraulic fracturing…have been widely reported as the reasons for the recent American oil and gas boom, neither of these is explanatory. In fact, the techniques are decades old. The boom emerged from smart drilling.”
Better data enables smarter drilling. But anyone with a digital camera or an iPhone knows that images gobble up storage capacity—and those are tiny images, compared to detailed seismic maps.
Three-dimensional seismic maps help oil and gas companies know where to drill and Apache Hadoop is an ideal platform for storing those images with their metadata. Storing seismic data from multiple experiences permits learning in the aggregate across all of those experiences. This improves a firm’s long-term return on investment, across multiple projects.
Watch our blog in the coming weeks for reference architectures in other industry verticals.
References
[1] Judith Hurwitz, et. al, Big Data for Dummies, John Wiley & Sons, Inc, 2013.