MultiQx-GPU: An Overview
To support concurrent query processing, MultiQx-GPU provides the functionalities needed by databases to coordinate GPU resource sharing. In this section we highlight the design principles and overall structure of the system.
The design of MultiQx-GPU abides by two main principles. The first one is versatility — the techniques presented by the system should be applicable to different GPU databases and computing frameworks for managing GPU resources. GPU database technologies are still evolving very quickly. Different systems have different query engine implementations and may be based on different GPU computing frameworks. The methods employed by MultiQx-GPU therefore should be easily utilized in all these variations. This requires the design of MultiQx-GPU to capture the essential properties of GPU query processing, to build upon the common abstractions of GPU frameworks, and to integrate with existing and future GPU database engines in a non-intrusive manner.
The second principle followed by MultiQx-GPU is high efficiency. Originally designed for gaming and super computing applications, GPU hardware and system software still do not have native support for multitasking. Basic system-level functionalities familiar to the CPU world, such as virtual memory (VM) and fine-grained context switches, are not provided by commercial GPU drivers. This forces MultiQx-GPU to add an extra layer of application-level software to support multi-query capabilities on its own, which, if not taken great care of, could incur high overhead.
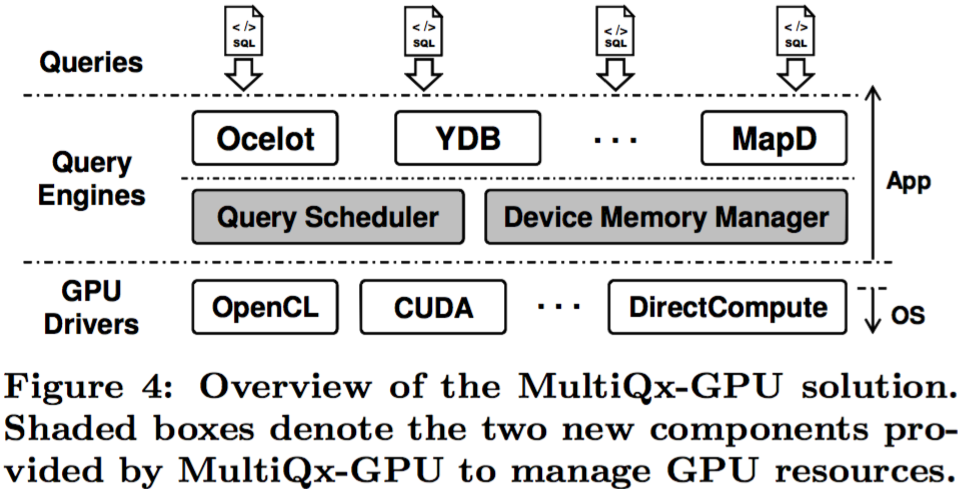
Figure 4 shows the position of MultiQx-GPU in the overall GPU database software stack. MultiQx-GPU is built into the database query engine, but remains loosely coupled with existing components in the query engine. It enforces controls over GPU resource usage by transparently intercepting the GPU API calls from user queries. This design does not change existing programming interfaces of the underlying GPU drivers, and minimizes the modifications to the other components of the GPU query engine. MultiQxGPU resides completely in the application space, and does not rely on any OS-level functionalities privileging to the GPU drivers. It can thus be easily ported between different query engine systems (such as Ocelot, YDB, and MapD [17]) and GPU computing frameworks (such as CUDA, OpenCL, and DirectCompute [19]) to enable GPU resource sharing.
MultiQx-GPU comprises two main components providing the support required for concurrent query executions. Working like an admission controller, the query scheduler component controls the concurrency level and intensity of resource contention on GPU devices. By controlling the queries that can execute concurrently at the first place, query scheduler maintains optimal workload on the GPUs that would maximize system throughput. Once a proper concurrency level is maintained, the device memory manager component further ensures system performance by resolving the resource conflicts among concurrent queries. Through VM-like automatic data swapping service, it makes sure that multiple queries with moderate resource conflicts can make concurrent progress efficiently without suffering query abortions or causing low resource utilization.
References
- Kaibo Wang, Kai Zhang, Yuan Yuan, Siyuan Ma, Rubao Lee, Xiaoning Ding, and Xiaodong Zhang. 2014. Concurrent analytical query processing with GPUs. Proc. VLDB Endow. 7, 11 (July 2014), 1011-1022. DOI=http://dx.doi.org/10.14778/2732967.2732976