Article Source
Workflow for ML Projects — MLOps
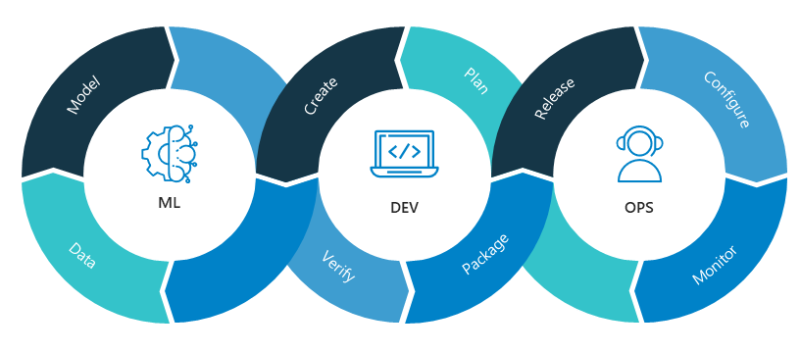
In one of my previous articles, i had mentioned the Agile Methodology **— An efficient way to engineer software solutions. **Agile/DevOps has a sibling in the data world — MLOps. MLOps consists of a set of practices that enable efficient and salable development and deployment of Machine Learning Solutions. In this article, we will see what MLOps is all about.
A peek into MLOps
Before we get started from atom, let us have an abstract view of what MLOps is. MLOps is an approach that is used to develop and deploy ML solutions efficiently. Just like DevOps, MLOps brings together Data Scientists, DevOps Engineers and Operations to develop, deploy, monitor and maintain ML solutions.
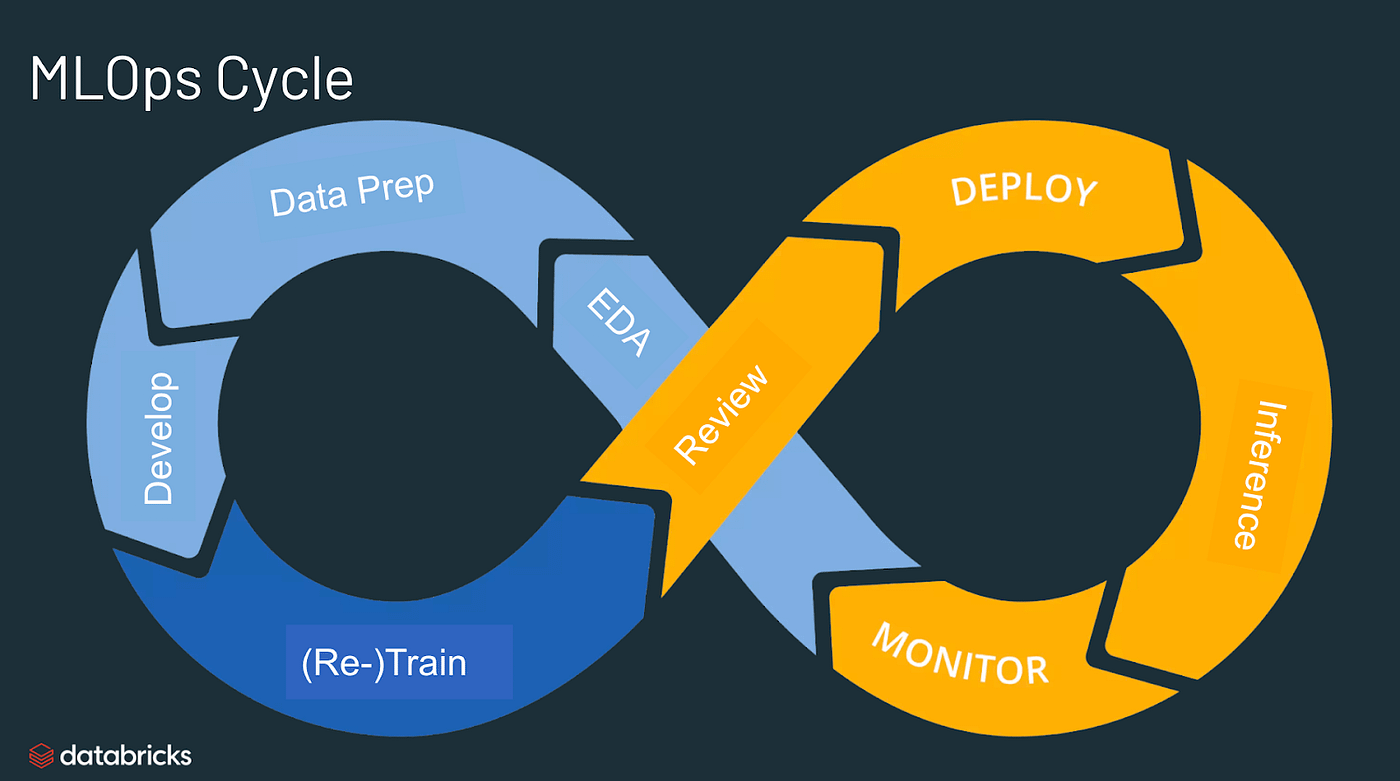 MLOps Cycle — https://databricks.com/glossary/mlops
MLOps Cycle — https://databricks.com/glossary/mlops
Why MLOps?
Let us see why to use MLOps. For complex tasks like Data Science, MLOps will provide better efficiency and becomes really critical especially when lot of diverse job roles are involved (Analysts, Data Engineers, ML Engineers etc.). Secondly, a typical ML Project will contain a large number of teams / engineers collaboration wherein each of their tasks have equal importance. In such situations, following a strict set of practices will provide better management efficiency.
Understanding MLOps cycle
Understanding MLOps cycle requires understanding of a data science project flow at first. From EDA till Monitoring and retraining, a typical data science project goes through 7 stages from start to end.
 https://databricks.com/glossary/mlops
https://databricks.com/glossary/mlops
EDA: Exploratory Data Analysis focuses on analyzing the data and gaining insights from it using visualizations. EDA is vital for understanding the data for ML as well as for gaining insights from data to make business decisions.
Data Preparation and Feature Engineering: Data is never assumed to be perfect and clean. Data Engineers are thus brought in to perform data engineering, performing cleaning and transformation and maintain consistency throughout the dataset. The whole accuracy of ML model depends on the cleanliness and consistency of the data. Hence, this becomes a vital step again.
**Model training and tuning: **ML model forecasts any value depending on the input given. This step focuses on training an ML model and fine tuning it until the desired performance is achieved. The core part here is often considered to be the fine tuning, since a model it is initial configuration might not provide fruitful results. Fine tuning employs a wide range of ML techniques to bring out the best with the given data.
Model review and governance: The generated model is tested for its accuracy and performance. If any organization specific policies are applicable, that too is evaluated here to ensure that the model is compliant. The usability of the model, especially it’s alignment with business problem and use case is evaluated.
Model Inference and Serving: This step focuses on setting up the technical infrastructure for model deployment — CI/CD pipelines, API Endpoints etc.
Model deployment and monitoring: Model is deployed to the developed cloud infra and is monitored for it’s performance and output.
Automated model retraining: Model training services on cloud takes up a given data and trains a model and optimizes to it’s best possible. This ensures that the model is up to date with the data and avoids the model getting outdated.
With the clarity in Data Science process, let us look at how an ML cycle with look like (Refer to diagram 2).
The team starts with EDA, goes to data preparation, develops model, trains or re-trains it, review the model, deploys it, inferences and monitors it. This cycle continues.
Thank you for reading!
Useful Links:
- Find me on LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/in/vishnuu0399
- Know more about Me: https://bit.ly/vishnu-u
- Read more on MLOps: https://databricks.com/glossary/mlops