Article Source
Modern Data Stack
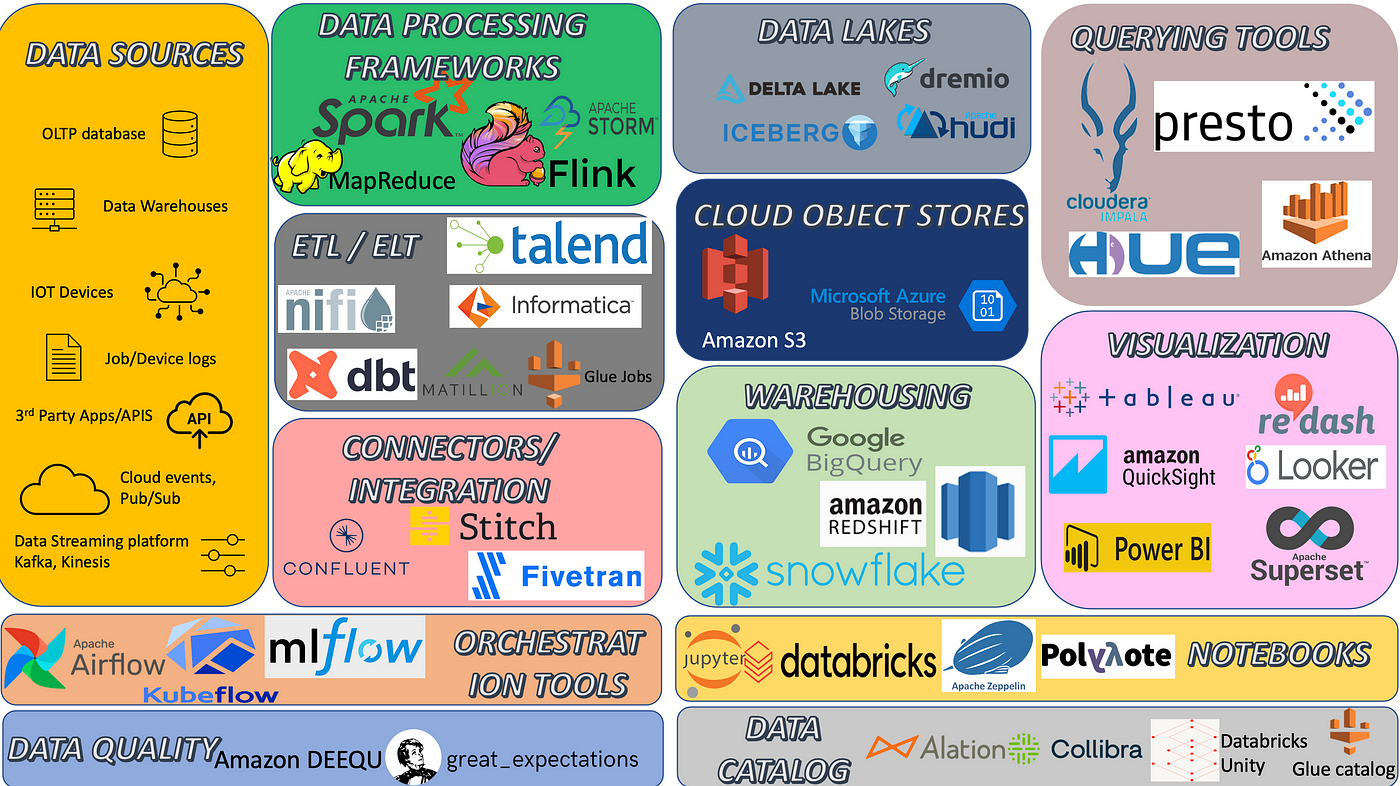 Data Stack
Data Stack
You might have seen multiple posts around this subject as time keeps evolving and bringing changes into tech stack, however this includes recent discovery in data processing frameworks, visualization tools, ETL tools, Development notebooks, Data catalog..etc
Over the time, we might have come across different terms like ETL, ELT, Reverse ETL. When it comes to database, jargon words that changed over time includes OLTP, OLAP, Big Data, Data Lake and Data Lakehouse..etc.
One of the highlighting difference between modern data stack and a legacy data stack is that modern data stack is cloud hosted and expects very less effort from users.
This post covers the list of tech stack in the picture in brief. It mostly covers the list of tools that I have come across in my experience. Let me know in comments section for any tools/frameworks that has been missed out.
Data Sources
Data, as we know, is massive, comprises of complex data sets and exists in various form. It can be of structured, semi-structured or unstructured form. Data is getting exploded like anything in last decade compared to the previous ones. Diverse data sources also plays a major role in recent years which ranges from social data, machine data, streaming events, transactional data…etc. Most of the data sources are capable of sending huge volumes of data in real-time.
Data Processing Frameworks
This term become popular after the introduction of Hadoop’s MapReduce framework. There were days when MapReduce framework was celebrated all over the world. However, within short span, some concerns in MapReduce framework was addressed through in-memory computations in Apache Tez and Apache Spark. In order to process real-time, frameworks like Flink, Samza and Storm have been introduced as well.
ETL/ELT
Tools used to ingest, transform and store curated data into target system. Modern day ETL tools changed a lot compared to traditional ETL which predominantly supports reading data only from transactional databases or data-warehouse. Traditional ETL is not scalable, undependable, expensive, and slow for the agile, data-driven modern organization. On the other hand, Modern ETL can also be called as Cloud ETL, due to the fact that modern ETL has evolved to execute jobs in cloud environment, which makes it scalable, fast and process data in real-time.
Connectors/Integrations
Recently, there are lot of connectors/integration tools developed to easily connect and ingest data from any cloud services, applications or system. Assists to quickly connect to critical enterprise applications, databases, and systems of records by using in-house or external connectors. It reduces the amount of effort and time required to transfer data from data source to other systems. Data Lakes
Data Lake, one of the latest approach to store all forms of data can be established in on -premises or in the cloud. All the cons of cloud file systems / object stores (S3, Azure Blob) like update & delete functionality, Time travel, ACID Transactions and Scalable metadata are the core functionalities of Data Lakes. Databricks, which recently introduced the Data Lakehouse term, has taken Spark journey to a higher level on data and Machine Learning.
Cloud Object Stores
Though cloud object stores like S3, Azure Blob, Oracle Filesystem, IBM Filesystem have been built based on the characteristics of Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS), cloud object stores have been improved a lot during the recent years. Most of the cloud object stores comes with an easy-to-use user interface and it’s secure, durable and enables cost efficiencies.
Warehousing
Compared to traditional data warehouses like Teradata and Oracle Analytics, modern cloud based warehouses are scalable and easy to implement in few hours. It has the characteristics of 1) bulk loading and unloading data which comprises of compressed files, different formats like JSON, Avro, ORC, Parquet..etc, 2) loading data from cloud file storage like S3, Azure Blob using the concept of external tables, 3) providing granular security model and sharing data between accounts in secured manner, 4) replicating data and preventing from failover.
Querying tools
Data stack can’t be completed without querying tools, which is the base editor for databases, datalakes..etc. Most of the tools leverage standard SQL as it’s query language for querying. However, Hue depends on Hive Query Language and Apache Pig needs Pig Latin Scripts for querying data. Irrespective of SQL or non-SQL, all the tools serves similar purpose of helping users to understand the data and it’s respective schema, summary of the table.
Visualization
Business intelligence (BI) combines business analytics, operational analytics, data mining, data insights, progress of data and best practices to help organizations to make data-driven decisions. Like other areas, Visualization also biased towards cloud. Most of the Visualization Dashboards can be created realtime instead of worrying about infrastructure and time associated with it. Recent additions like Superset and Redash makes a good competition in this area along with existing tools like Tableau, Looker, Quicksight..etc
Orchestration tools
This covers scheduling and monitoring part of production jobs once the initial development phase has been completed. Airflow and Luigi have been popular for a while and then Kubeflow and Databricks’s MLFlow were added. Though all these tools serves common need, every tool has a highlighting feature which stands out compared to other orchestration tools.
Notebooks
Other than IDE, Notebook is one of the popular development environment for most of the Data Engineers, Machine Learning Engineers and Data Scientists. Primarily, Notebook is used to develop Spark code through Scala or Python programming. It also supports execution of SQL query, shell scripts and other utilities. Few notebooks like Databricks also supports to deploy the code directly into production environment (Live Tables, MLFlow).
Data Quality
Testing on datasets is always one of those aspects that people overlook. Amazon DeeQu and Great Expectations helps to unit-test the data by offering some automated profiling on our data and generating some tests automatically. It helps to verify the quality of many large production datasets within stipulated amount of time.
Data catalog
It supports data search, innovation, discovery and a repository of metadata on information sources from across the enterprise, including data sets, business intelligence reports, visualizations, and conversations. Data catalog becomes more popular during the introduction of Hive catalog in Big Data environment. In traditional data stack, data catalogs were primarily used to help developers more quickly find and understand data. But modern data catalogs are used to provide wider range of data intelligence solutions including data analytics, governance and data discovery.